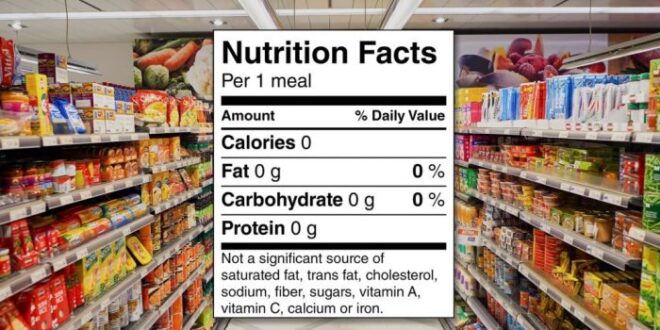
Food with zero calories list: Ever dreamt of indulging in delicious treats without the guilt of extra calories? This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of zero-calorie foods, exploring their nutritional profiles, potential benefits, and hidden pitfalls. Prepare to be amazed (and maybe a little skeptical) as we uncover the truth behind these seemingly magical edibles.
We’ll navigate the intricacies of these foods, from the surprisingly common to the more obscure, examining their potential impact on your diet and overall well-being. Get ready to unlock the secrets of satisfying your cravings without compromising your health goals.
Types of Zero-Calorie Foods
Zero-calorie foods play a significant role in various dietary strategies, often used for weight management or specific dietary needs. Understanding the types of zero-calorie foods and their nutritional profiles is crucial for informed choices. These foods, while offering little to no caloric value, can still contribute to a balanced diet by providing essential micronutrients and fiber in some cases.
Common Zero-Calorie Foods
A variety of foods fall into the zero-calorie category, encompassing different food groups and textures. This section lists some commonly consumed zero-calorie foods, offering insight into their composition and potential benefits.
- Water: A fundamental component of the human body, water is essential for numerous bodily functions and is calorie-free. Its lack of calories makes it a popular choice for hydration and weight management. Water supports overall health and is critical for cellular processes.
- Unsweetened Beverages: Many beverages, including plain black coffee, unsweetened tea, and diet soda, are calorie-free. However, it’s important to note that the absence of calories doesn’t negate the potential impact of artificial sweeteners or other ingredients.
- Plain Vegetable Broth: Vegetable broth, when prepared without added fats, sugars, or other high-calorie ingredients, often falls into the zero-calorie category. This makes it a suitable choice for those seeking low-calorie soup options or for adding flavor to dishes.
- Air-Popped Popcorn: Unbuttered, unseasoned air-popped popcorn is a good source of fiber and is often considered calorie-free, offering a satisfying snack. Its low calorie content makes it a favorable choice for those looking to manage calorie intake.
- Certain Spices and Herbs: A wide range of spices and herbs, including paprika, cumin, oregano, and thyme, possess minimal caloric value and are widely used to enhance the flavor of dishes.
Nutritional Composition
The nutritional composition of zero-calorie foods varies significantly. Some, like water, primarily provide hydration, while others may offer trace amounts of vitamins and minerals. It is crucial to understand that zero calories doesn’t equate to zero nutrients.
- Water: Primarily provides hydration, essential for various bodily functions. It doesn’t contain any calories, vitamins, or minerals.
- Unsweetened Beverages: May contain minimal amounts of naturally occurring vitamins and minerals or negligible amounts of those present in the plant material. However, the addition of artificial sweeteners is common, which can have varying health effects.
- Vegetable Broth: May contain trace amounts of vitamins and minerals, primarily depending on the vegetables used in the broth. Often low in calories but high in flavor.
- Air-Popped Popcorn: Provides a good source of fiber, contributing to digestive health. The fiber content is crucial for gut health and satiety.
- Spices and Herbs: Contribute primarily to flavor enhancement with minimal nutritional content. Some spices contain trace amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Comparison of Zero-Calorie Foods
The sensory experiences of zero-calorie foods can differ significantly, impacting their appeal and usability in various dietary contexts.
| Food Type | Taste | Texture | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Neutral | Liquid | Essential for hydration | Can become monotonous for some |
| Unsweetened Beverages | Varying (e.g., coffee, tea) | Liquid | Hydration, flavor | May contain artificial sweeteners, potentially impacting health |
| Vegetable Broth | Savory, depends on ingredients | Liquid | Flavor enhancer, potential source of minerals | May not be filling enough for some |
| Air-Popped Popcorn | Neutral | Crunchy | Fiber, potential for satiety | Can be bland without seasoning |
| Spices and Herbs | Wide range, depending on the spice | Varying | Flavor enhancement, potential for some vitamins/minerals | Can become overwhelming in high quantities |
Dietary Considerations and Implications
Zero-calorie foods, while seemingly beneficial for weight management, can have various implications on overall health. Understanding these implications is crucial for responsible consumption and maintaining a balanced diet. Their role in diverse dietary approaches warrants careful consideration.While zero-calorie foods can be part of a healthy eating strategy, they shouldn’t replace nutrient-rich foods. Excessive reliance on them can lead to nutritional deficiencies and other potential health issues.
A balanced approach incorporating a variety of foods is key to optimal health.
Potential Health Implications
The potential health implications of zero-calorie foods need careful consideration. Their lack of nutritional value, while beneficial for weight management, can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. This can impact digestion, energy levels, and overall well-being. For instance, relying solely on zero-calorie sweeteners might lead to a deficiency in important nutrients found in natural sugars.
This can result in metabolic imbalances or other related health issues.
Risks of Excessive Consumption
Excessive consumption of zero-calorie foods can present various risks. A diet overly reliant on these foods may lead to nutrient deficiencies, impacting overall health. This can include deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, potentially impacting bone health, immune function, and energy levels. Moreover, the body’s natural response to certain zero-calorie sweeteners, especially in excess, can lead to digestive discomfort or other related symptoms.
Maintaining a balanced diet with sufficient amounts of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is crucial to prevent such issues.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet is paramount for optimal health. A balanced diet should include a wide variety of foods from all food groups, providing essential nutrients for proper bodily functions. It is important to recognize that zero-calorie foods, while helpful in certain contexts, cannot fully replace the nutritional benefits of a balanced intake of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
The overall composition of the diet, including a diverse range of food groups, is key to maintaining health.
Role in Various Diets and Eating Patterns
Zero-calorie foods can play a role in various diets and eating patterns, often as part of a weight management strategy. However, their role should be carefully considered, especially in relation to the overall dietary plan. For example, some low-calorie diets may incorporate zero-calorie substitutes for sugar, but it’s essential to ensure adequate nutrient intake from other food sources.
In certain cases, zero-calorie sweeteners can be a viable alternative to sugar, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to reduce their sugar intake. Their use, however, should be part of a larger dietary strategy that considers the entire nutritional profile of the diet.
Dietary Recommendations
The table below provides a summary of dietary recommendations concerning zero-calorie foods. These recommendations highlight the importance of a balanced approach.
| Category | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Overall Diet | Prioritize a balanced diet incorporating a wide variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups. |
| Zero-Calorie Foods | Use zero-calorie foods as part of a comprehensive dietary plan, not as a replacement for essential nutrients. |
| Nutrient Intake | Ensure sufficient intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber from natural food sources. |
| Portion Control | Practice mindful portion control, even with zero-calorie foods, to avoid potential imbalances. |
| Professional Guidance | Consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice. |
Practical Uses and Applications

Zero-calorie foods, while not providing energy, play a valuable role in various dietary strategies. Their use extends beyond simply satisfying hunger pangs; they offer specific benefits in managing calorie intake and crafting delicious, healthy meals. Understanding these practical applications allows for informed choices and the effective integration of these foods into a balanced diet.Zero-calorie foods can be powerful tools in weight management strategies by aiding in the creation of lower-calorie meals.
They can replace higher-calorie components without compromising taste or nutritional content. This is particularly helpful in achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Careful consideration of portion sizes and overall dietary context is crucial for maximizing the benefits of these foods.
Zero-Calorie Foods in Weight Management
Zero-calorie foods are instrumental in various weight management strategies, as they contribute to reduced calorie intake without sacrificing satisfaction. They act as effective substitutes for calorie-dense foods, allowing individuals to experience a sense of fullness while consuming fewer calories. This strategy can be particularly beneficial in conjunction with regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Incorporating Zero-Calorie Foods into Recipes
Zero-calorie foods offer versatility in culinary applications. They can enhance the taste and texture of dishes without adding unwanted calories. These ingredients can be used to replace or complement calorie-rich counterparts, leading to healthier alternatives without compromising flavor. Careful selection and preparation are key to ensuring the optimal integration of these foods into a wide variety of recipes.
Examples of Zero-Calorie Food Substitutions
Several zero-calorie foods can effectively replace calorie-rich ingredients in various dishes. For example, using unsweetened beverages instead of sugary drinks can dramatically reduce calorie intake. Similarly, substituting plain broth for cream-based sauces significantly lowers the calorie count in soups and stews. These are just a few examples of how zero-calorie ingredients can contribute to healthier eating choices.
Sample Recipes with Zero-Calorie Foods
| Recipe | Zero-Calorie Ingredient | Calorie-Rich Ingredient Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Cucumber and Dill Salad | Cucumber slices | Mayonnaise dressing |
| Zesty Tomato Soup | Vegetable broth | Cream of tomato soup |
| Lemon Herb Chicken Breast | Lemon juice | Heavy cream sauce |
| Black Bean Burgers | Water | Fatty ground beef |
| Fresh Fruit Salad | Fruit pieces | High-calorie fruit toppings |
These examples demonstrate how zero-calorie ingredients can be seamlessly integrated into existing recipes, resulting in healthier and more satisfying meals. The table above provides a concise overview of potential substitutions, allowing for a practical understanding of how these foods can be applied in various culinary contexts.
Misconceptions and Controversies

Zero-calorie foods, while offering potential benefits in weight management, are often surrounded by misconceptions and controversies. These products, frequently marketed as a shortcut to a healthier lifestyle, can be misinterpreted as a solution to complex dietary needs. Understanding these misconceptions and controversies is essential for making informed choices about incorporating zero-calorie foods into one’s diet.The marketing strategies employed for zero-calorie foods can sometimes lead to unrealistic expectations and potential negative consequences.
The portrayal of these products as magic bullets for weight loss or as a complete dietary solution can be misleading and detrimental to a balanced approach to nutrition.
Common Misconceptions
A common misconception revolves around the idea that zero-calorie foods are inherently healthy. While they may contribute to reduced caloric intake, they often lack essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals crucial for overall health and well-being. Focusing solely on caloric content without considering nutritional completeness can lead to dietary deficiencies. For example, a diet solely comprised of zero-calorie sweeteners might lack fiber, essential vitamins, and other nutrients.Another prevalent misconception is that zero-calorie foods are a risk-free alternative for individuals with specific dietary needs or medical conditions.
Their suitability should be assessed individually with a healthcare professional to avoid potential adverse interactions or unintended consequences. For example, certain zero-calorie sweeteners may not be suitable for individuals with specific metabolic conditions.
Controversies Surrounding Use and Marketing
The marketing of zero-calorie foods often employs strategies that promote an idealized body image and can potentially create unrealistic expectations about weight loss. Such marketing tactics can negatively impact individuals’ self-esteem and mental health, especially when they focus on achieving an unrealistic ideal weight. Furthermore, the marketing of these foods as a substitute for whole foods might contribute to a skewed understanding of healthy eating habits.Zero-calorie sweeteners have been linked to concerns regarding potential long-term health implications.
While studies have not definitively proven these links, continued research is crucial to understanding the possible relationship between their use and health conditions. For example, some studies have suggested a potential association between the consumption of certain zero-calorie sweeteners and digestive issues.
Ever looked for a zero-calorie food list? It’s kinda tough to find something totally calorie-free, right? I mean, sure, air is technically zero calories, but that’s not exactly filling. Speaking of weird food, have you seen those candy corn salt and pepper shakers? They’re pretty cool, but probably not on any serious zero-calorie food list.
Still, finding those truly calorie-free foods is a fun quest, and definitely something to consider when you’re trying to watch your intake.
Potential Negative Impacts of Marketing Strategies
Marketing strategies focusing on the calorie-free aspect of a product might unintentionally detract from the importance of a balanced diet and whole foods. This approach may promote an unhealthy focus on the absence of calories rather than the presence of essential nutrients. Such marketing may inadvertently lead to a dependence on processed foods, rather than a balanced approach to healthy eating.The portrayal of zero-calorie foods as a guaranteed path to weight loss can lead to unrealistic expectations and disappointment.
Individuals might experience frustration and disillusionment if their weight loss goals are not achieved solely by consuming these products.
Importance of Critical Thinking, Food with zero calories list
Critical thinking plays a crucial role in evaluating information about zero-calorie foods. Consumers should scrutinize the information presented, assess the source’s credibility, and consider potential biases. This includes looking beyond marketing claims and seeking out unbiased scientific evidence. For instance, a marketing campaign may focus on specific benefits without mentioning potential drawbacks or side effects.
Comparative Analysis of Claims
| Claim | Supporting Evidence | Counterarguments |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-calorie foods are a safe and effective way to lose weight. | Some studies show that zero-calorie sweeteners can help with weight management. | A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial for weight loss. Zero-calorie foods alone may not be sufficient. |
| Zero-calorie sweeteners are harmless. | Many zero-calorie sweeteners are approved by regulatory bodies. | Long-term health effects of zero-calorie sweeteners are still under investigation. |
| Zero-calorie foods are a healthy alternative to calorie-laden foods. | They can help reduce calorie intake. | Zero-calorie foods may lack essential nutrients found in whole foods. |
Food Safety and Preparation: Food With Zero Calories List
Proper handling and preparation of zero-calorie foods are crucial for ensuring safety and preventing potential health risks. These foods, often composed of ingredients with minimal nutritional value, are still susceptible to contamination and spoilage. Adhering to safe food handling practices is essential regardless of the calorie content of the food.
Safe Handling and Preparation Procedures
Safe food handling procedures for zero-calorie foods are largely the same as for any other food. These procedures aim to prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms and the contamination of food with pathogens. Cleanliness is paramount throughout the entire process, from initial ingredient selection to final consumption. Proper handwashing, sanitization of surfaces, and using separate cutting boards for different food types are all critical components of safe food preparation.
So, I was looking into foods with zero calories, and it got me thinking about dog food. Like, Blue Buffalo puppy dog food here is totally packed with nutrients, but it’s not exactly calorie-free, right? Back to the human food with zero calories list—still gotta find that perfect snack!
Employing these practices will ensure the safety and quality of zero-calorie foods.
Preserving Zero-Calorie Foods
Several methods can be used to preserve zero-calorie foods for extended periods. Proper storage conditions and appropriate preservation techniques are essential for maintaining the quality and safety of these foods. Freezing, dehydration, and canning are common methods for preserving zero-calorie foods. Each method has specific requirements to ensure food safety and prevent spoilage. Careful attention to these methods is crucial to extend the shelf life of these foods.
Nutritional Value of Preparation Methods
The nutritional value of zero-calorie foods is inherently low. Food preparation methods, however, can sometimes impact the overall quality and safety of these foods. While these methods don’t significantly alter the nutritional profile, they can affect the texture, taste, and overall appeal of the food. Different cooking methods can impact the bioavailability of certain components, but for zero-calorie foods, these effects are negligible.
Examples of Preparation Methods
Zero-calorie foods can be prepared in various ways to suit different tastes and preferences. They can be incorporated into various dishes, from salads and soups to stir-fries and main courses. These foods can also be used as flavor enhancers or textural components. Simple preparations, such as chopping or shredding, are common for incorporating them into recipes. More complex methods like stir-frying or grilling can also be used to create unique and appealing dishes.
Food Safety Guidelines
| Food Type | Handling Precautions | Preservation Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-calorie sweeteners (e.g., aspartame, sucralose) | Store in airtight containers in a cool, dry place. Avoid excessive heat. | No specific preservation methods required, but maintain proper storage conditions to avoid deterioration. |
| Zero-calorie vegetables (e.g., certain lettuce varieties) | Wash thoroughly to remove dirt and contaminants. Use separate cutting boards for these items. | Refrigerate promptly to maintain freshness. Freezing is a viable preservation option. |
| Zero-calorie protein substitutes (e.g., some protein powders) | Follow manufacturer’s instructions for storage and preparation. | Store in airtight containers in a cool, dry place. Freezing is a suitable preservation method. |
Illustrative Examples
Zero-calorie foods offer a diverse range of options for individuals seeking to manage their caloric intake. Understanding their visual characteristics, textures, and preparation methods can aid in incorporating them into various diets and meal plans. This section provides detailed descriptions of these foods, highlighting their potential as part of a balanced dietary approach.
Visual Appeal and Sensory Characteristics
Zero-calorie foods, though lacking in calories, often possess appealing visual characteristics. Their textures, colors, and aromas can enhance the overall dining experience. The visual appeal, coupled with specific flavors and aromas, can contribute to a satisfying meal.
- Cucumber Slices: Crisp, translucent slices of cucumber, ranging from pale green to a slightly yellowish-green depending on variety, offer a refreshing visual appeal. The texture is firm and cool, providing a refreshing crunch when consumed. The subtle vegetal aroma adds a light, crisp flavor profile, and the water content contributes to a feeling of hydration.
- Steamed Spinach: A vibrant, deep green color characterizes steamed spinach, which can be served as a side dish or incorporated into other preparations. The texture is tender-crisp, almost melting when cooked, with a subtle, earthy aroma that complements many other flavors. The vibrant green color contrasts nicely with other ingredients in a dish, making it a visually appealing addition.
- Celery Sticks: Celery sticks are a classic example, offering a pale green hue. The crunchy texture, combined with the light, slightly sweet, and slightly herbaceous aroma, provides a pleasant contrast to other, more substantial foods. The pale green color makes them a versatile ingredient in various dishes.
Zero-Calorie Food Preparations
Zero-calorie foods can be incorporated into a variety of dishes, contributing flavor and texture without impacting calorie intake. Their preparation methods often depend on the specific food item and desired outcome.
- Celery and Carrot Sticks with Hummus: Celery and carrot sticks, thinly sliced, are served with a dollop of hummus. The crisp texture of the vegetables contrasts with the smooth, creamy texture of the hummus. The mild flavor of the hummus complements the slightly sweet and earthy flavors of the vegetables, creating a healthy and satisfying snack. The vegetables provide a vibrant visual appeal, while the hummus adds a creamy contrast.
- Watermelon Salad with Mint: A vibrant watermelon salad, incorporating diced watermelon, fresh mint leaves, and a light vinaigrette, offers a refreshing and visually appealing dish. The juicy texture of the watermelon contrasts with the slightly peppery and aromatic mint. The intense red color of the watermelon is complemented by the bright green of the mint leaves. The refreshing aroma and flavors make this a light and flavorful option.
- Broth-Based Soups with Zero-Calorie Vegetables: Zero-calorie vegetables like zucchini, bell peppers, and mushrooms can be used in flavorful broth-based soups. The light texture of the vegetables in the broth creates a balanced meal, offering a satisfying, yet low-calorie, option. The various colors of the vegetables add visual interest, enhancing the appeal of the dish.
Dietary Preferences and Needs
Zero-calorie foods can be incorporated into various dietary preferences and needs. Their versatility allows for adaptability in various meal plans.
- Vegetarian and Vegan Diets: Many zero-calorie vegetables are naturally compatible with vegetarian and vegan diets. They can be used as sides, additions to main courses, or even the main course itself in creative preparations.
- Weight Management: Zero-calorie foods can be used to increase portion sizes or add visual appeal without impacting calorie intake, contributing to a sense of fullness and satiety.
- Allergies and Intolerances: Many zero-calorie vegetables are naturally free from common allergens and intolerances, making them suitable for individuals with specific dietary restrictions.
Summary Table of Visual Characteristics
| Food Item | Color | Texture | Aroma |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cucumber | Pale green to yellowish-green | Crisp, firm | Subtle vegetal |
| Spinach | Deep green | Tender-crisp | Earthy |
| Celery | Pale green | Crunchy | Slightly sweet, herbaceous |
| Watermelon | Red | Juicy | Sweet |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, while zero-calorie foods can offer a unique approach to dietary choices, a balanced perspective is key. Understanding the nuances of these foods, their limitations, and the importance of overall dietary balance will empower you to make informed choices. Remember, moderation and mindful consumption are always crucial.
Question & Answer Hub
What are some common misconceptions about zero-calorie foods?
Many people believe zero-calorie foods are a magic bullet for weight loss. The reality is more nuanced. While they can be part of a balanced diet, they aren’t inherently a substitute for healthy eating habits.
Are all zero-calorie foods created equal?
No. Different zero-calorie foods offer varying sensory experiences and nutritional compositions. Some might be a refreshing addition, while others might feel bland or lacking in taste.
Can zero-calorie foods help with weight management?
Potentially, yes, but they shouldn’t be the sole focus. Zero-calorie foods can be incorporated into a weight management strategy, but a holistic approach that includes balanced nutrition and exercise is always more effective.
What are the potential risks of consuming too many zero-calorie foods?
Excessive consumption of any type of food, including zero-calorie foods, could potentially lead to nutritional deficiencies if not part of a well-rounded diet. Prioritize a variety of foods for optimal health.
 Nimila
Nimila